Autoantibodies: Patient test assays
How to efficiently detect autoantibodies?
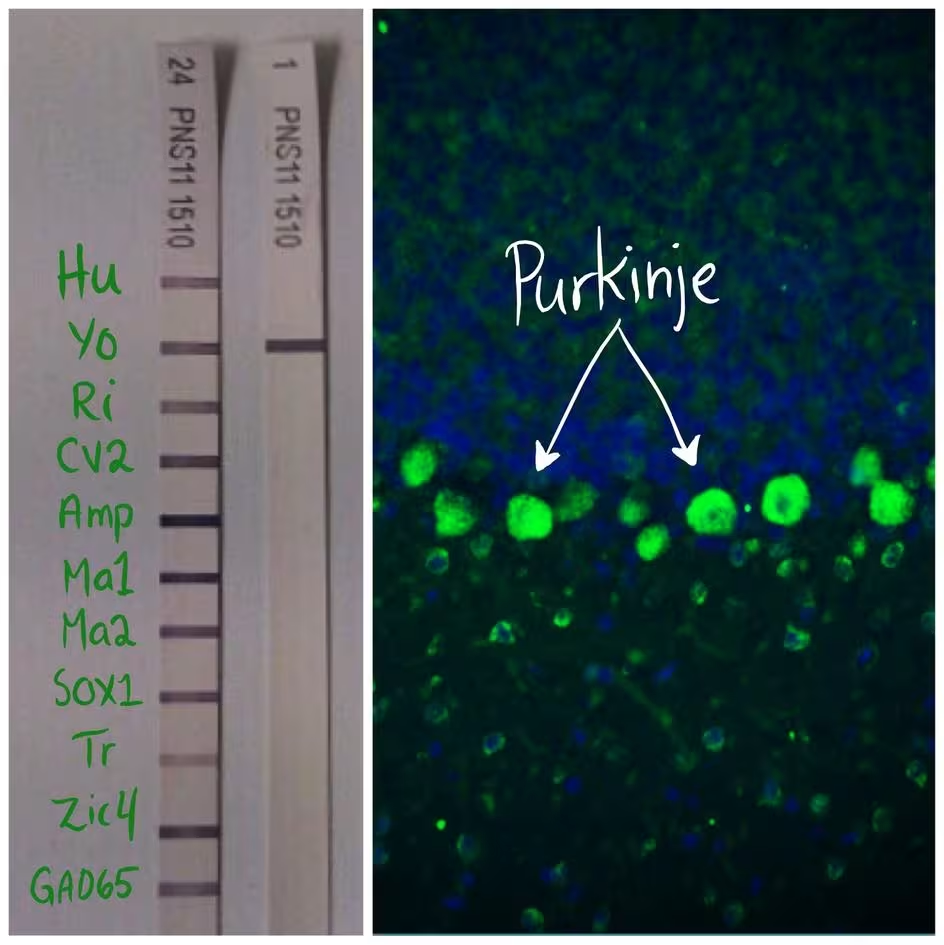
About the research project
We perform most of the neuroimmunology tests in Norway. For the detection of onconeural antibodies we use line blots and immunohistochemical analyses of cerebellar tissue. Currently, we are able to test 11 different antibodies related to paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (PNS). These are mainly antibodies causing ataxia by targeting the neuronal population of the cerebellum (Medusa head ataxia (external link)).
Three groups of autoantibodies can be delineated according to the neuronal localization of the targeted antigen:
Group 1: Nuclear and cytoplasmic neuronal antigens (NCNA)
- Anti-Hu [ANNA-1]
- Anti-Ri [ANNA-2]
- Anti-Yo [PCCA-1]
- Anti-Ma1/2 [PNMA-1/2]
- Anti-CV2/CRMP5
- Anti-Sox1 [AGNA]
- Anti-Zic4
- Anti-Gephyrin
- Anti-GABARAP
All these antibodies, except GABARAP, are associated with PNS and their frequency is rare: a European study conducted during 8 years was able to compile less than 1000 cases and incidence is estimated being about 0.01 % of all cancers. [PMID:20212230 (external link); DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2009.341 (external link)]
Group 2: Cell-surface synaptic antigens (CSSA)
- Anti-NMDAR
- Anti-Lgi1
- Anti-Caspr2
- Anti-GABABR
- Anti-AMPAR
- Anti- VGCC
- Anti-GlycineR
- Anti-Tr/DNER
- Anti-mGluR1
- Anti-mGluR5.
Patients with CSSA-Abs share common features: (I) symptoms seem to be related to the disruption of the target antigen by the antibodies; (II) symptoms can be reversed by immunotherapy more commonly than in patients with NCNA-Abs; (III) the association with malignancy is much less consistent; (IV) neurological symptoms are similar to a pharmacological blockade of the recognized antigen.
Group 3: Intracellular synaptic antigens (ISA)
- Anti-GAD65
- Anti-Amphiphysin
Both ISA targeted antigens are located in the presynaptic terminal of neurons, a region where antibodies can reach cytoplasmic proteins. Moreover, immune response seems to imply both cellular and humeral compounds.
A new approach is that we are looking at exosomes which are small, extracellular vesicles released by cells in the body. These contain various molecules including proteins, lipids and RNA. Cancer cells release exosomes which promotes growth and metastasis of the tumour, as well as suppresses the immune system. As exosomes circulate in the blood, they serve as a promising source of new biomarkers of disease. We are analysing the RNA content of serum exosomes from patients with ovarian cancer and PCD to identify new biomarkers which can help improve diagnosis of PCD.
Yo
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Cerebellar ataxia
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Uterus cancer
The onconeuronal Yo antibody binds to two different proteins; cerebellar degeneration-related protein 2 (CDR2) and 2-Like (CDR2L). These proteins are quite similar and have around 50 % sequence homology. Quite little is known about their location, interaction partners, regulation and function in neuronal cells. In the cerebellum the proteins are expressed in Purkinje neurons and cells of the moleculare layer (probably stellate and/or basket cells), but they are also expressed in neuronal cells in the midbrain (PMID:27253404 (external link)).
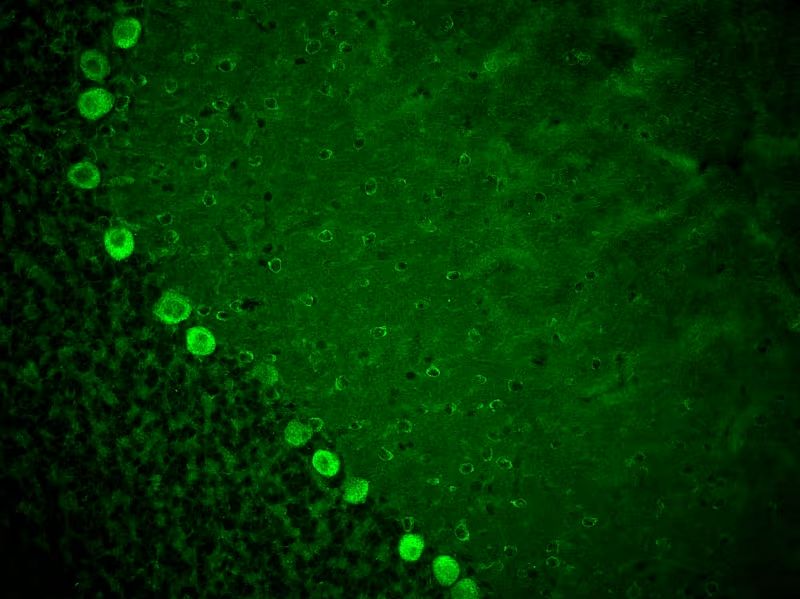
Hu
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Sensory and autonomic neuropathy
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Encephalomyelitis
- Limbic encephalitis
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Small-cell lung cancer
- Non-small-cell lung cancer
- Extrapulmonary small-cell cancer
HuD or ELAV-like protein 4 is an RNA-binding protein only present in the nuclei of neurons. HuD binds to U-rich sequences in the 3_UTRs of several mRNAs including c-fos, tau, p21waf1, N-myc, and GAP-43 to control stability and expression of these mRNAs. It is thought to be important for neuronal development and in some cases for plasticity in the mature brain.
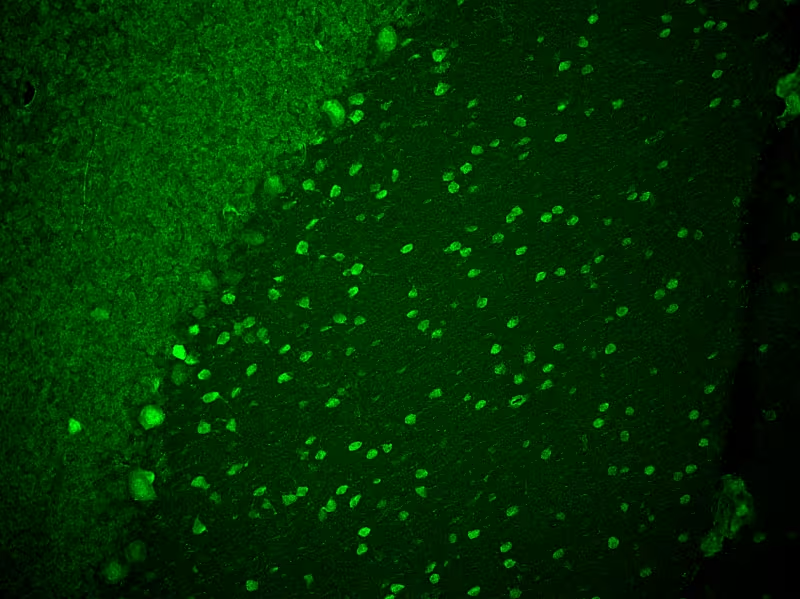
Ri
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Brainstem encephalitis (incl. opsoclonus-myoclonus-syndrome)
- Cerebellar ataxia
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Breast cancer
- Small-cell lung cancer
- Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland
The antigen target of anti-Ri is unknown. In cerebral cortex neuronal extract, anti-Ri reacts with two antigens at 55 kDa and 80 kDa. In cerebellar sections anti-Ri shows a similar staining pattern like anti-Hu.
CV2
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Sensory and sensorimotor neuropathy
- Encephalomyelitis
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Limbic encephalitis
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Chorea
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Small-cell lung cancer
- Thymom
CV2/CRMP5 = collapsing response mediator protein 5 belongs to the family of cytosolic Ulip/CRMP proteins involved in axon guidance and neurite outgrowth signaling during neural development. CRMP5 is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane and plays an important role in mitophagy. CRMP5 can be found in the cytoplasm of oligodendrocytes.
Amphiphysin
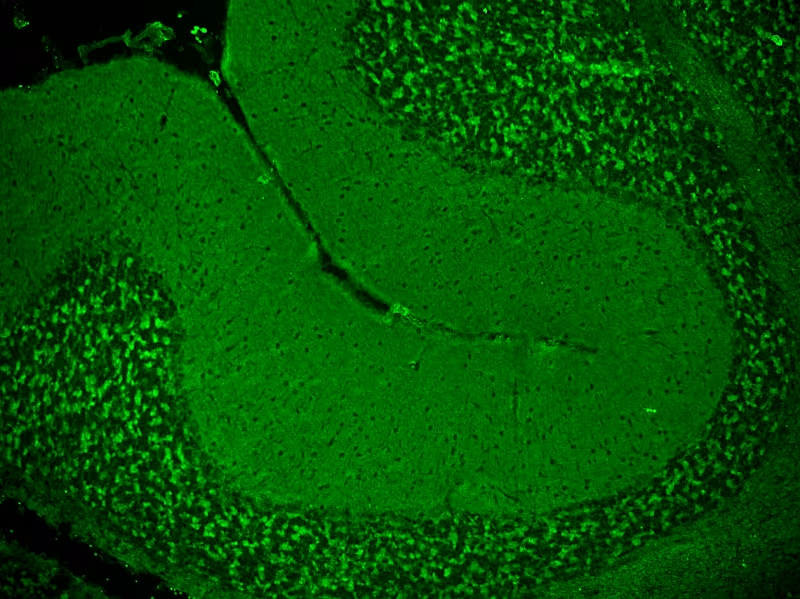
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Stiff-person-syndrome
- Various symptoms
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Breast cancer
- Small-cell lung cancer
Amphiphysin belongs to the superfamily of Bin–Amphiphysin–Rvs (BAR) domain proteins, which are membrane shapers and related to clathrin-mediated endocytosis because they provide extended membrane-binding interface to modulate membrane topologies. Neurons using the BAR domain superfamily members to perform synaptic formation and postsynaptic reorganization processes including receptor endocytosis and recycling as well as the structural (re)organization of synapses. [PMID:26285709 (external link); DOI: 10.1242/jcs.174193 (external link)]. In the cerebellum, amphiphysin is found in presynaptic nerve terminals of the granule as well as molecular cell layer.
Ma1
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Limbic encephalitis
- Brainstem encephalitis
- Cerebellar ataxia
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Testicular cancer
- Lung cancers
PNMA1 = paraneoplastic antigen Ma1 is a 37 kDa neuron and testis-specific protein. PNMA family modulates apoptosis. http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8ND90 (external link); [PMID:10050892 (external link)].
Ma2

Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Limbic encephalitis
- Brainstem encephalitis
- Cerebellar ataxia
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Testicular cancer
- Lung cancers
PNMA2 = paraneoplastic antigen Ma2 is a 40 kDa brain-specific protein. http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UL42 (external link); [PMID:10362822 (external link); DOI:10.1056/NEJM199906103402303 (external link)].
SOX1
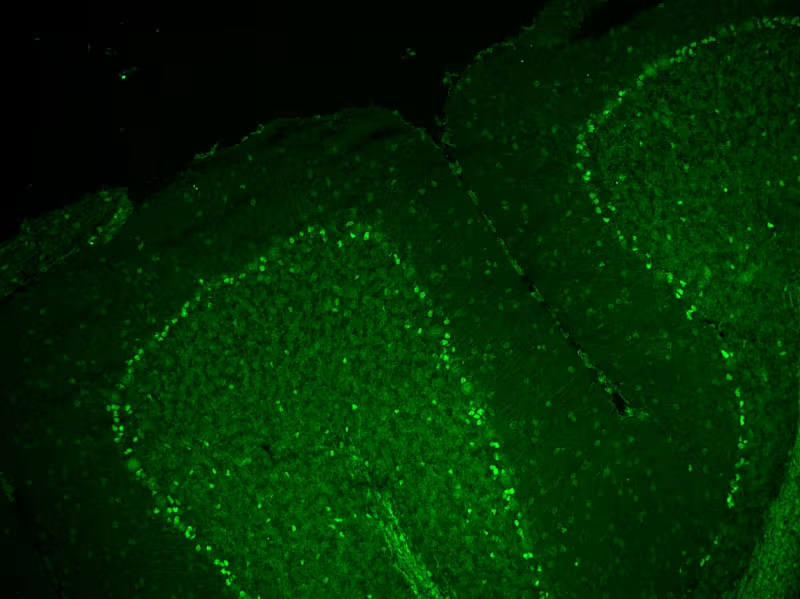
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Lambert Eaton Myasthenia gravis
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Small-cell lung cancer
SOX1 = SRY-related high mobility group box 1 is neuronal stem cell marker and an intracellular transcription factor expressed in Bergman glia cells of the adult cerebellum. Anti-SOX1 reactivity is often associated with either Hu, VGCC, CV2/CRMP5 and amphiphysin antibodies.
Tr
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Cerebellar truncal and limb ataxia
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Hodgkin Lymphoma
DNER = Delta/Notch-like epidermal growth factor-related receptor is the target antigen of autoantibody Tr. Anti-Tr antibodies are defined by a specific staining pattern in cerebellar tissue that is characterized by punctate immunoreactivity in both the dendritic tree and soma of Purkinje neurons but not in their axons. [PMID: 25745634 (external link)]
Zic4
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Cerebellar degeneration
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Small-cell lung cancer
Zic 4 = zinc-finger protein 4 of the cerebellum belongs to the family of five Zic genes, each encoding a highly related zinc-finger transcription factor. Zic4 is restricted expressed in the granule cell neurons of the cerebellum and interacts with Gli proteins to regulate Shh signaling an important factor for neuronal development and function.
GAD65
Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS) associated with this antibody:
- Stiff person syndrome
- Limbic encephalitis
Most frequently associated tumors:
- Non-paraneoplastic
GAD65 = glutamic acid decarboxylase enzyme links two neurotransmitter systems by catalyzing the decarboxylation of glutamate to synthesis GABA. GAD65 protein is mainly located in GABAergic axon terminals where it is functionally coupled to transport of GABA into synaptic vesicles and thereby mainly responsible for neurotransmission. In the cerebellum, Golgi cells in the granule layer expressing strongly GAD65 and Gad65-containing terminals are scattered within the neurophil or surrounding cell bodies and dendritic arborisation of the Purkinje neu

