PCD: Neuroprotective drugs
Autoantibody uptake: from Fc receptors to calcium signaling?
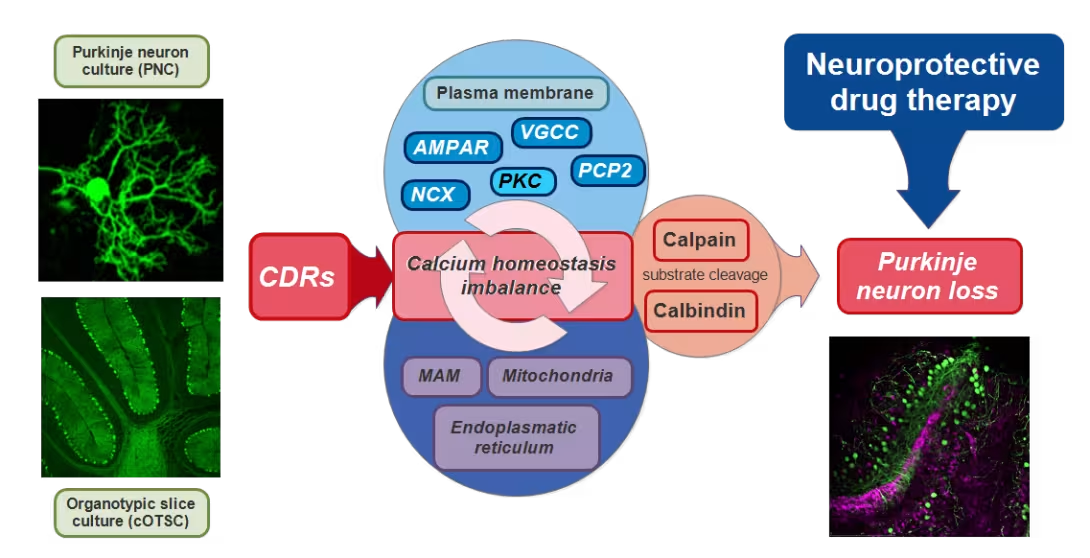
About the research project
To this date, there is no cure for the progressive neuronal loss seen in PCD patients. Even though removal of the tumor prevents further neuronal damage, it does not reverse the existing neurodegeneration and leaves the patients in severe disabled state, which is a burden both economically and socially. Our objective is to develop ex-vivo and in-vivo PCD models where we can pharmacologically target single molecules which are negatively affected by the CDR antibody binding. Investigating the drug effects not only on a cellular level but also at the entire CNS/body level will be the first milestone towards clinical trials regarding PCD related neuroprotective therapy.
Neuroprotective compounds
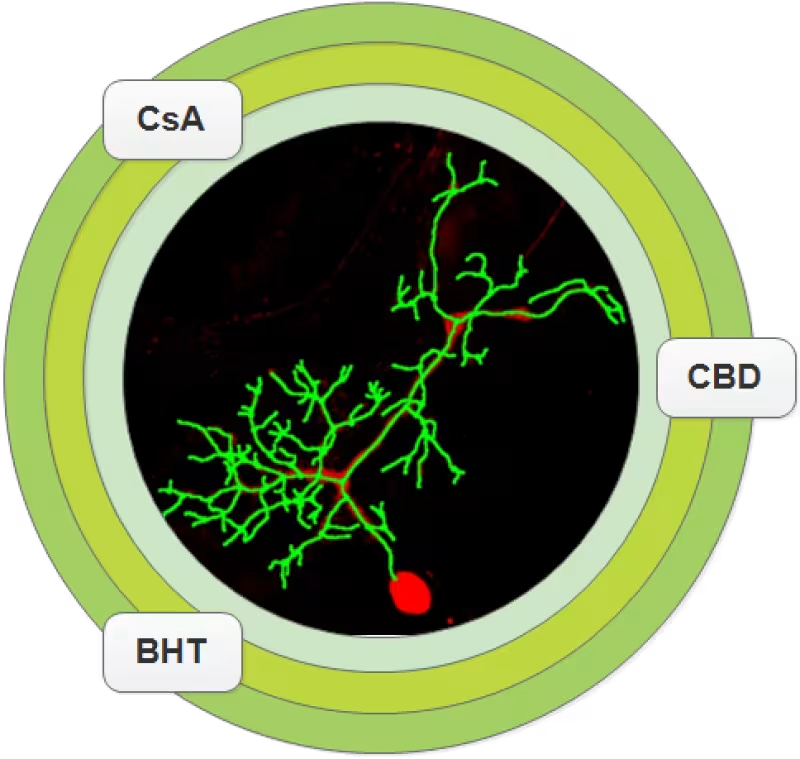
As current immunomodulatory therapies for Yo antibody-mediated PCD are not very effective, additional therapeutic strategies addressing in particular the Purkinje neurone degeneration are important forfuture PCD therapy. Our recent findings demonstrate that using compounds such as cyclosporin-A (CsA), cannabidiol (CBD) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) that addressing calcium homeostasis imbalanceand ROS over-production seems to provide a high neuroprotective potential for Purkinje neurons ex vivo (doi: 10.1111/nan.12492).

