Breast cancer-on-a-chip model for testing of nanomaterials

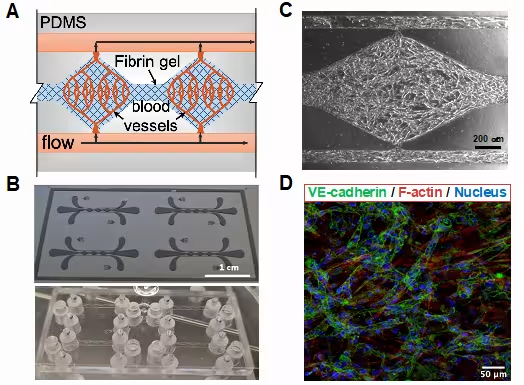
Microfluidic chip for breast cancer-on-a-chip model. Cartoon depicting the different components and cells integrating the breast cancer-on-a-chip model (top-left). Microfluidic chip (bottom-left). 3D reconstruction of HUVEC microvasculature and adjacent MFC10a cancer cell monolayter in the breast cancer chip (right). Empty liposome (Lip-SiR) were perfused in the HUVEC channel for 24 hr. For both cell lines the nucleus is shown in blue (DAPI), membrane in magenta (WGA-AF488) and empty liposome in green (Lip-SiR). Top, merged channels DAPI/WGA-AF488/Lip-SiR. Middle, merged channels DAPI/Lip-SiR. Bottom, single channel for Lip-SiR. White arrows indicate Lip-SiR signal.
Lung-on-a-chip model for testing of nanomaterials
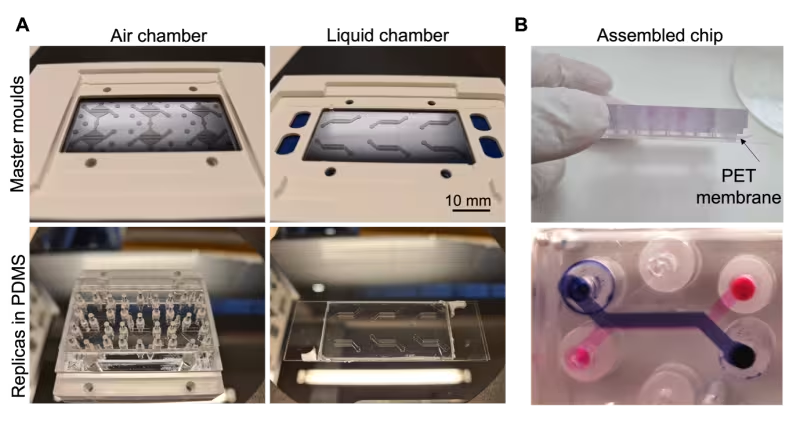
A) master moulds and replicas in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) of top (air) and bottom (liquid) chambers that compose the lung-on-a-chip model. Master moulds were fabricated using photolithography. B) Side view (top) and magnification (bottom) of the fully assembled chip. The air and liquid chambers are interfaced by a thin (20 um) PET microporous membrane comprising 3 um pores.