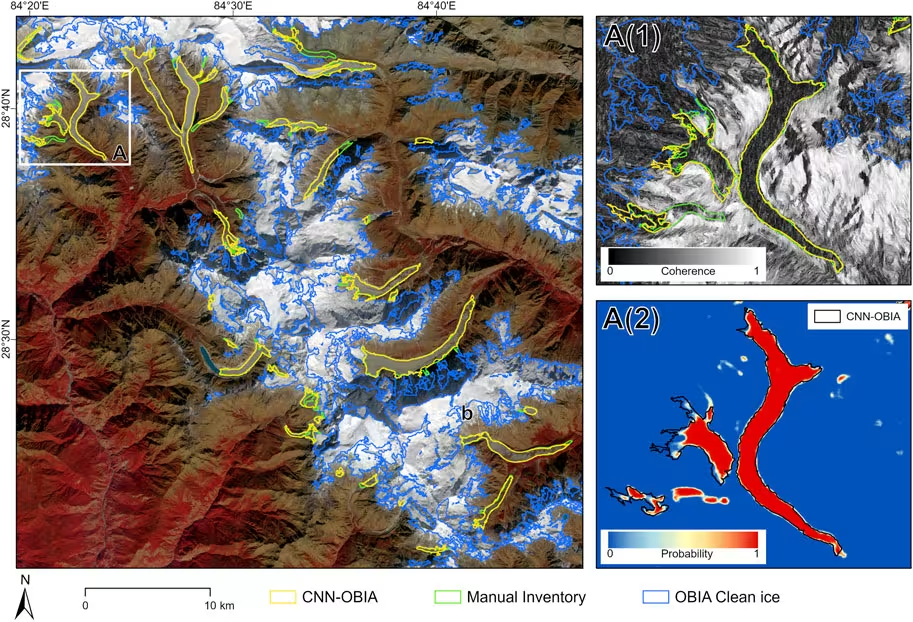
About the method:
Machine learning and GeoAI enable automated, large-scale analysis of geospatial data, allowing efficient detection, mapping, and monitoring of surface features and processes that are difficult and time-consuming to identify using traditional methods.
In particular, deep learning approaches—most notably convolutional neural networks (CNNs)—are well suited for learning subtle spectral, spatial, and contextual patterns from remote sensing data. Once trained, these models can reliably identify and map a wide range of Earth surface features. This includes distinguishing clean ice from debris-covered glaciers, detecting rock glaciers and moraines with complex textures, identifying crevasses and flow structures, and characterizing snow and ice properties such as extent, roughness, or surface condition.
By integrating information across multiple data sources and spatial scales, these models are especially effective in heterogeneous and challenging environments where traditional mapping approaches are impractical or infeasible.
Machine learning and GeoAI significantly enhance our ability to monitor Earth surface processes, exploit extensive remote sensing archives, and improve understanding of environmental change across space and time.