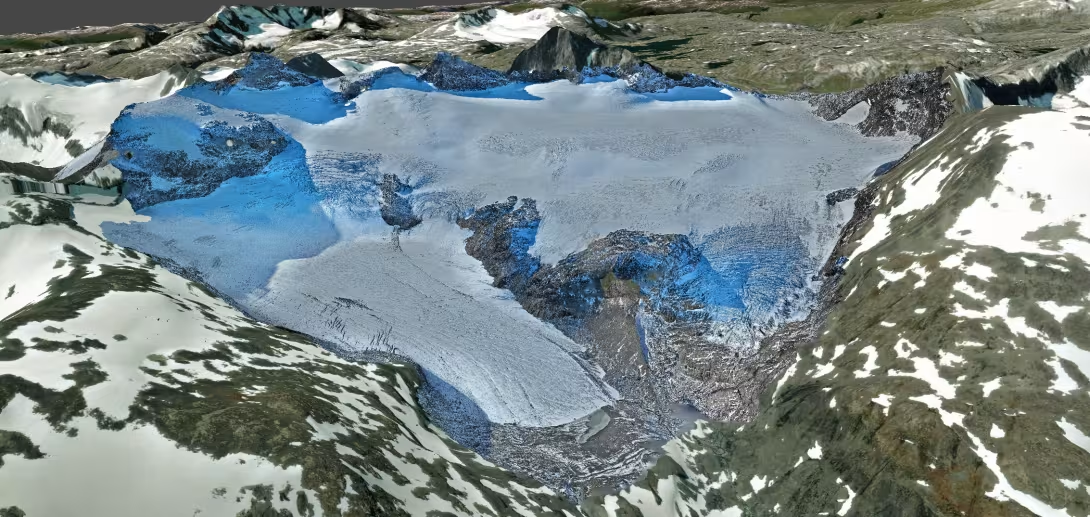
About the method:
Photogrammetry is a powerful method for creating 3D products from a series of overlapping 2D images, including historical aerial photographs, drone (UAV)- and satellite imagery. By processing these datasets, it is possible to create high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs), orthomosaics, point clouds, and 3D meshes that accurately represent the Earth’s surface at specific points in time.
A key application of photogrammetry is change detection: by comparing high-resolution DEMs for different time periods, it is possible to detect, quantify, and visualize a wide range of environmental and structural changes over time. This approach is often used for monitoring glacier changes, and for mapping landslides and erosion.
Accurate change detection relies on proper co-registration, in other words, the precise alignment of DEMs from different periods. Misalignment can introduce significant errors, so it is essential to ensure datasets match in all three spatial dimensions. Tools such as the XDEM Python package provide advanced functionality for DEM co-registration, DEM differencing, and statistical analysis, enabling more reliable and meaningful results.
Overall, photogrammetry-based change detection is an efficient method for studying processes and dynamics across a wide range of environments and timescales.