ALOFT Cloud Characterization Instruments
Overview of the AMPR, CRS, EXRAD and CoSSIR cloud characterization instruments.
Advanced Microwave Precipitation Radiometer (AMPR)
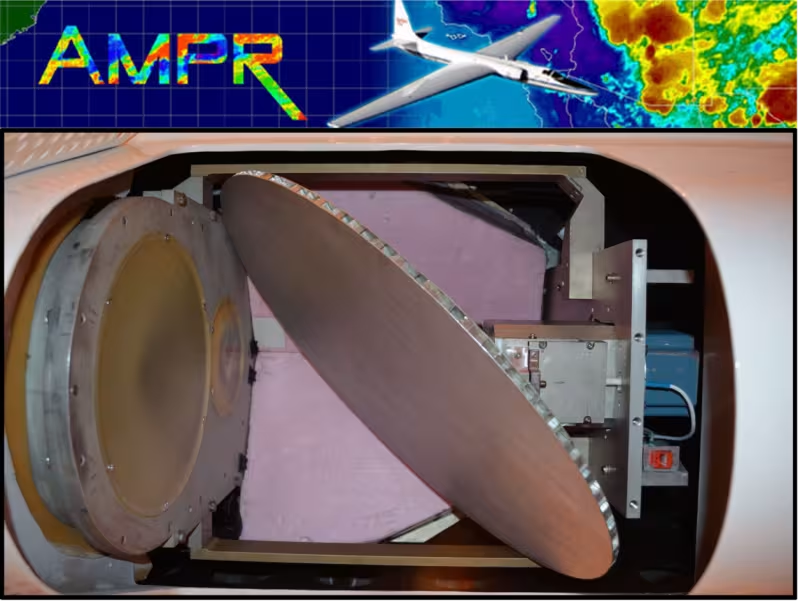
The Advanced Microwave Precipitation Radiometer (AMPR) passively measures total power at 10.7, 19.35, 37.1, and 85.5 GHz. It scans cross-track with two orthogonally polarized channels per frequency, mapping out a ~40-km wide swath below the ER-2 as it flies. Within this swath AMPR can retrieve vertically integrated information about precipitation, ice and liquid water contents, atmospheric water vapor, and winds near the ocean surface. AMPR’s role in ALOFT is to measure the structure, evolution, and environment of thunderstorms that produce gamma-ray glows and TGFs.
More information about AMPR can be found at: https://weather.ndc.nasa.gov/ampr/ (external link)
PI: Timothy L (external link)ang (external link)
Co-PI: Corey Amiot
Cloud Radar System (CRS)

The CRS is a 94 GHz (W-band; 3 mm wavelength) Doppler radar developed for autonomous operation in the NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft and for ground-based operation. It provides high-resolution profiles of reflectivity and Doppler velocity in clouds and has important applications to atmospheric remote sensing studies.
Read more about CRS here (external link). | Scientific article on CRS (external link)
X-band Radar (EXRAD)
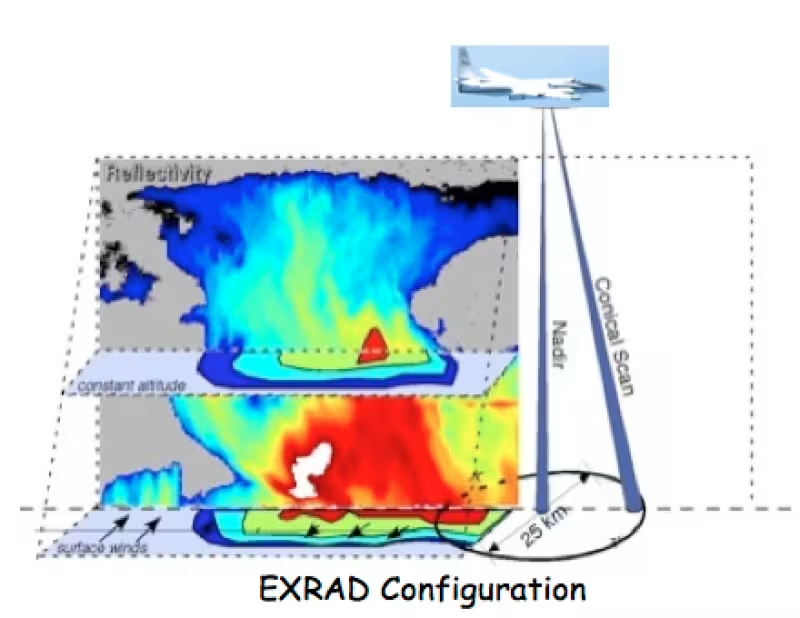
- X-band Doppler radar to replace EDOP
- Conical scanning and fixed nadir beams
- 3D precipitation and wind measurments
- Ocean surface winds
- Operation from ER-2 or Global Hawk
- For studies of atmospheric composition and tropical storms as well as providing validation for GPM and ACE missions
Link to website (external link) | Scientific article (external link)
Conically Scanning Sub-millimeter-wave Imaging Radiometer (CoSSIR)

The Configurable Scanning Submillimeter-wave Instrument/Radiometer (CoSSIR) is an airborne, 16-channel total power imaging radiometer that was primarily developed for the measurement of ice clouds.

